Hydrogeological characterization of the Complex Terminal aquifer using geoelectrical investigation in the arid environment of Chetma-Biskra (South-East of Algeria)
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
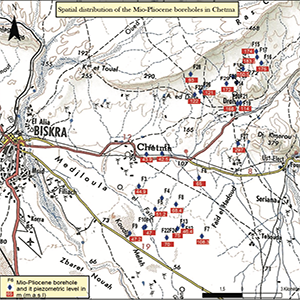
As a transition hydrogeological area, Biskra (Algeria) holds large groundwater resources in deeply buried aquifers such as the Complex Terminal. Due to a growing demand of drinking water supply and irrigation combined to low recharge, this arid region is facing an acute shortage of water and hence, the need for groundwater investigation. We used an integrated approach including geophysical investigation correlated to the geological and hydrogeological context in the Chetma area. The results highlight a deep structural form with significant hydrogeological features. In fact, two resistant limestone anticlines called Droh corresponding to a piezometric dome and a syncline filled with conductive deposit materials were identified. The Maastrichtian formation, consisting of fractured limestone, about 200 to 350 m thick, together with Lower Eocene marl limestone and limestone form a complex aquifer. At more than 400 m depth, boreholes capturing Maastrichtian limestone offer a high yield ranging from 25 to 90 L/s. Moreover, groundwater yield provides an average of 40 L/s at 300 m of depth. In contrast, synform geometries with high clay and marl content offer a weak groundwater yield. We confirmed the occurence of fractured aquifers which could constitute potentially groundwater production zones. This study provides new insights to enhance groundwater pumping for domestic and irrigation purposes for 2030.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.














