Qualitative evaluation of groundwater in terms of its suitability for drinking and irrigation. The case study of Sidi-Bel-Abbes alluvial aquifer (NW Algeria)
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Accepted: 28 July 2023
Authors
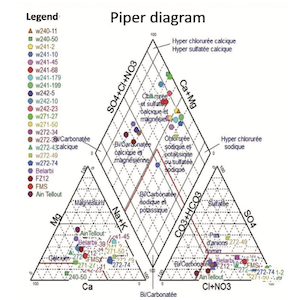
Sidi-Bel-Abbes province is a semi-arid area mainly used for agricultural activity in northwestern Algeria. Its groundwater resources are characterized by high salinity varying from one area to another. This work aims at improving our understanding of these waters, through hydrochemical classification, to define their chemical facies and monitor their spatial evolution. In addition, this groundwater’s quality is assessed regarding their suitability for drinking and irrigation. The obtained results showed that the groundwater of the Sidi-Bel-Abbes area is dominated by chlorides, particularly the chloride calcium and sodium facies. Indeed, the spatial distribution of the different chemical facies confirmed the contribution of adjacent hydrogeological units and the interaction between the groundwater and the Mekerra Wadi. In terms of suitability for drinking, the maximum chemical element concentration accepted by the Algerian legislation is exceeded in most samples, especially for nitrates, chlorides, sodium and calcium. The interpretation of Riverside and Wilcox diagram revealed that the alluvial groundwater of Sidi-Bel-Abbes is generally characterized by a high salinity with a low to medium alkalinity danger. Therefore, the quality of this water is medium to poor, suitable for irrigation, but under certain conditions. Also, the groundwater is unsuitable for sensitive plants because of its high chloride (Cl) ion content. Moreover, the results obtained indicate that the use of these waters in irrigation presents low sodium risks, and therefore are not likely to modify the structure of the soils in the Sidi-Bel-Abbes plain or reduce their permeability.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.












